Optical design consultancy based in Japan
Design methodology overview
Akira Yabe has created an optical design methodology
 that gives outstanding results, both in terms of sheer system performance and in manufacturability.
that gives outstanding results, both in terms of sheer system performance and in manufacturability.
The core of the process is an efficient global optimisation. This is accompanied by an efficient zoom lens prototyping method.
Aspherics & glass selection are given special consideration, and the design is desensitised to manufacturing errors in order to give the loosest possible tolerances for manufacture, consistent with maintaining quality in the real systems.
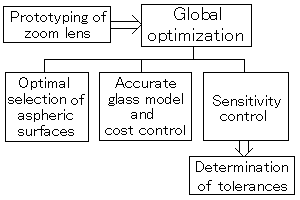
Global Optimisation
The use of an efficient global optimisation technique enables Akira to find the best solutions [the escape function methodology is used]:
- The appropiate lens type is created automatically by the global optimization. The result of the global optimization does not depend on the starting point very much. For the most cases parallel plates are enough for the starting point.
- Only the glass count need to be given. By trying a few values of the glass count the appropriate glass count is determined.
- All the practical design conditions are included from the beginning. The quality of the lens is directly expressed by MTF.
- The global optimization with escape function is very fast and the result is reliable.
- This method works very well even for the zoom lens, aspherics, and DOEs.
Prototyping of zoom lens
Akira developed a unique prototyping method of zoom lenses.
- For the zoom system there is a wide variety of zoom types. With this prototyping method various zoom types are created systematically.
- Existing lens data is not necessary for the starting point of the optimization.
- The global optimization is then applied to each zoom type and the best zoom type is determined.
Optimal selection of aspheric surfaces
Akira developed a unique method to determine which surface[s] should be aspherised.
Aspheric surface numbers are extended to continuous variables and the best aspheric surface numbers are determined by the conventional optimization.
Accurate glass model and cost control
Akira uses the accurate glass model including the abnormal dispersion. With this glass model exotic glasses are used very effectively.
The glass cost is also controlled. This allows the minimum use of expensive glasses.
Sensitivity control
The sensitivity to manufacturing errors is controlled [including tilt, decenter, thickness error, curvature error, and surface irregularity] throughout the design. The method is applicable to both high NA & wide field lenses.
As an added bonus, no additional calculation time is necessary for this desensitisation.
Determination of tolerances
Tolerances are determined rigorously from the performance statistics. Account is taken of the manufacturing costs.
The final tolerances are verified and the distribution of the quality is assessed by Monte Carlo methods.
Traveling group separation
In an optical system with many lens groups, the lens number of each lens group is extended to a real number and included in the independent variables of the optimization.
The best configuration of a zoom lens is automatically determined for the given total lens number and total group number.
Other functions of design program
- Universal target expression applicable for various lens designs
- Automatic determination of clear apertures for the required relative illumination
- Automatic selection of real glasses without the loss of performance
- Automatic selection of test plates without the loss of performance
- Systematic search and control of the ghost images in a short time